You may be wondering what diabetes and eyesight have in common. The truth of the matter is that people often underestimate problems and conditions that can arise due to diabetes. Diabetic eye problems are a major concern for many people with diabetes and should not be overlooked. It is recommended that those with diabetes have an eye exam done after their diagnosis and regularly after that.
It’s estimated that around 40-45% of Americans with diabetes have some form of diabetic eye problems. Many of these individuals may not even know that they have eye problems caused by diabetes either. This means that their condition may be getting worse to the point where it is irreversible.
In this article, we’ll discuss why high blood sugar can cause eye problems, what the issues entail, and how to prevent eye problems caused by diabetes.
How Can High Blood Sugar Affect Eyesight?
Individuals contending with diabetes will have an elevated blood sugar compared to individuals that do not have diabetes. This high blood sugar level can significantly impact eyesight and can cause severe eye problems down the road. One of the first signs of diabetes, or elevated blood sugar, is blurry vision. At the time of my own diagnosis, I noticed that I began to struggle to see PowerPoints clearly in school. Words on a page started to become blurred together. Little did I know that my blood sugar was dangerously low.
The reason why high blood sugar causes blurry vision is due to the many small blood vessels in your eyes being damaged by hyperglycemia. This causes fluid to leak into the retina, which leads to swelling. The tissue swelling around the retina causes blurry vision. This condition is known as macular edema. Diabetic macular edema can lead to blindness if it is left untreated.
Common Diabetic Eye Problems
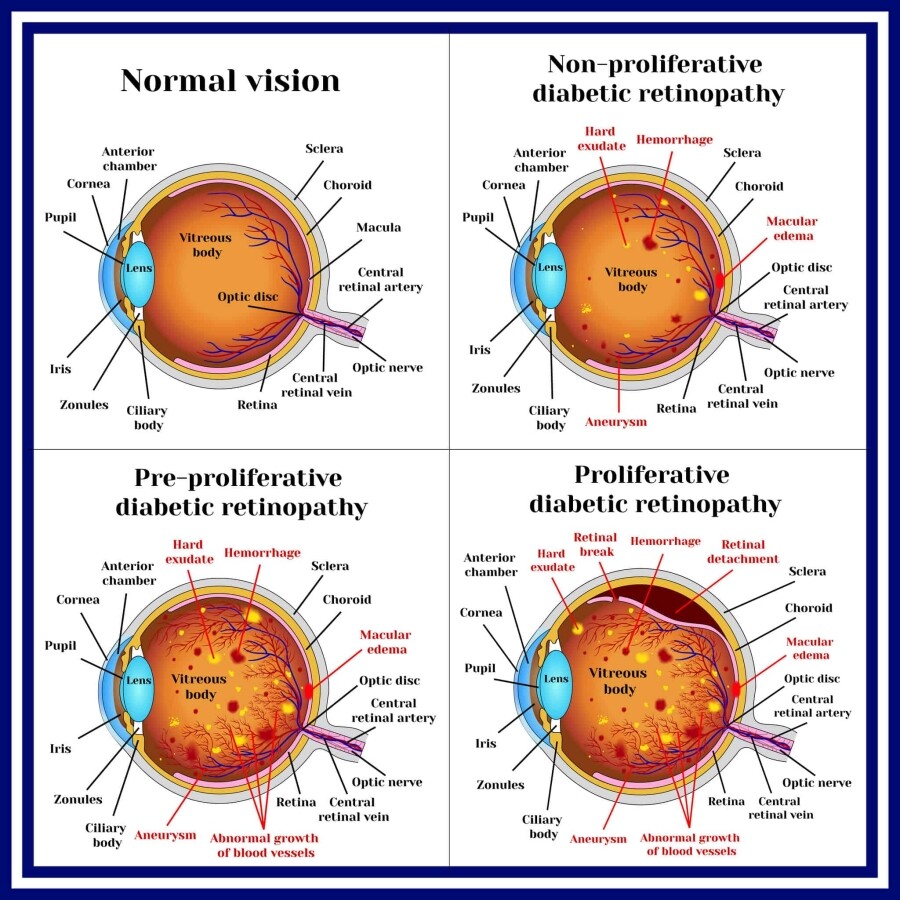
There are a few eye problems caused by diabetes that fall under “diabetic retinopathy.” This is a term used to describe retinal disorders caused by high blood sugar. Diabetic retinopathy is described as having damage to the blood vessels in the light-sensitive tissue of the retina. Regardless of the type of diabetes that you have, you may be at risk. One of the first signs of diabetic retinopathy is blurry vision.
Diabetic eye problems are directly related to the blood vessels being blocked due to high blood sugar and the blood vessels not getting proper blood flow. This results in the retina not getting appropriately nourished.
Glaucoma
Those with diabetes are twice as much at risk for having glaucoma than those without diabetes. Glaucoma is the leading cause of blindness for individuals over the age of 60. This condition is defined as the optic nerve being damaged due to pressure in the eye. This pressure in the eye is generally caused by fluid buildup. The fluid buildup can either be caused by an overproduction of fluid or damage to the drainage system. Typically, the fluid in the eye is drained through tissue known as trabecular meshwork. So, if fluid cannot be adequately drained, it will begin to buildup leading to increased pressure. Symptoms of glaucoma to look for include:
- Patchy blind spots
- Tunnel vision
- Eye pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Severe headache
- Halos around lights
- Eye redness
- Blurred vision
Cataracts
Individuals with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts at a younger age than those without diabetes. Cataracts are defined as the lens of your eye becoming cloudy, which affects your vision. This condition is common among older adults and generally develops slowly. Surgery is an option to treat severe cataracts, which involves removing the old lens and replacing it with an artificial lens. Other treatments for this condition include getting new glasses, wearing anti-glare glasses, or using a magnifying glass. Symptoms of cataracts include:
- Faded colors
- Blurry or cloudy vision
- Double vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Frequent prescription changes to glasses
- Glare or halo around lights
- Trouble seeing well at night
Four Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
1. Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy
During this stage, the tiny blood vessels in your retina will develop bulges called microaneurysms. The bulges may cause small amounts of blood to leak into the retina. You may not notice changes to your vision during this stage and typically does not need treatment. However, controlling your blood sugar levels and seeing an eye doctor regularly may prevent the damage to the eye from becoming worse.
2. Moderate Nonproliferative Retinopathy
Changes to the retina can occur at this stage due to swelling beginning in blood vessels. The swelling restricts the amount of blood flow through the blood vessels. Therefore, the retina is unable to get the proper nutrients that it needs. This can lead to diabetic macular edema. At this stage, you may notice vision problems when it comes to reading or driving.
3. Severe Nonproliferative Retinopathy
This stage is described as the blood vessels in the retina becoming blocked. So, the eye is no longer receiving the blood flow it needs, and scar tissue can begin to develop. The lack of blood flow triggers new formation of blood vessels. During this stage, individuals may develop macular ischemia, which is a condition described as the blood vessels closing off completely. You may experience blurry vision and dark spots or “floaters” during this stage.
4. Proliferative Retinopathy
New, yet Abnormal and fragile blood vessels begin to grow during this stage due to the lack of nourishment to the eye. Due to the new blood vessels being weak, they can cause additional bleeding in the eye, creating more scar tissue. This can lead to blindness.
What Increases the Risk of Diabetic Eye Problems?
Factors other than diabetes can put you at a higher risk for these eye problems. Having conditions such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, tobacco use, and pregnancy can increase your risk. Having a previous eye injury or eye surgery may also increase your risk for cataracts. Using certain medications for a more extended period of time, such as corticosteroids, can put you at a higher risk. There have been studies showing that African Americans are at a greater risk of developing eye problems such as glaucoma as well.
When to See a Doctor About Diabetic Eye Problems
Seeing your eye doctor on a regular basis is important, especially if you feel you may be suffering from diabetic eye problems. Reporting issues, such as blurry vision or eye pain, early on, can be what prevents you from having a worsened condition. Having eye problems may also be an indication of an underlying condition that you don’t yet know about. Visiting your doctor can bring this to light and allow you to receive the treatment you need.
Preventing Diabetic Eye Problems
The best way to prevent your risk of developing eye problems caused by diabetes would be to control your blood sugar levels. Managing your diabetes takes work and discipline. Monitoring your food intake and your level of physical activity daily is a step in the right direction.
On top of this, check your blood sugar levels often. You will not know how well you are managing your diabetes if you do not know the trends and averages of your blood sugar. Gain control of your blood pressure and cholesterol levels if you don’t already have control. This, again, means monitoring your food intake and learning how to lose weight if you need to.
Talk to your doctor about what medications might be required to lower your blood pressure. If you smoke or use tobacco, consider taking steps to quit. Talk to your doctor about what resources they may have to help you with that process. Lastly, consult your doctor. Your doctor will be able to assess you and the needs specific to you. This will be able to give you the most up to date information and resources when it comes to diabetic eye problems.
Conclusion
We hope that this has given you a little more insight into the eye problems caused by diabetes. It’s always crucial that you consult your doctor for advice related to your specific condition and symptoms. Consult your doctor to determine what medications are right for you to help you get your health back on track. Here at Prescription Hope, we know it can be difficult to afford medications that are meant to save your life and help you live better. That is why we work with over 180 pharmaceutical manufacturers to help you afford the medicine you need.
Enroll with us to find out if you are eligible to pay only $70.00 a month through Prescription Hope’s medication access service for each of your medications.