Function of the Thyroid Gland – Overview, Problems, Symptoms, Treatment
Posted by Prescription Hope - See Editorial Guidelines (Last Updated On: Tue Apr 25 2023)
The thyroid gland is an essential gland in the body and plays a significant role in regulating functions. However, problems can occur with the thyroid, forcing some individuals to get placed on medications. In this article, we will discuss the function of the thyroid and common problems that may occur with the thyroid. Before getting into the detail, though, here is a brief explanation. The Function of the Thyroid Gland: The thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly and located at the front of the neck. The thyroid produces three hormones, which are triiodothyronine, tetraiodothyronine, calcitonin. The thyroid steadily releases these hormones into the bloodstream to help the body regulate metabolism and the growth and development of the body. Now that you have a brief understanding, here is everything you need to know about the thyroid gland.
What is the Thyroid?
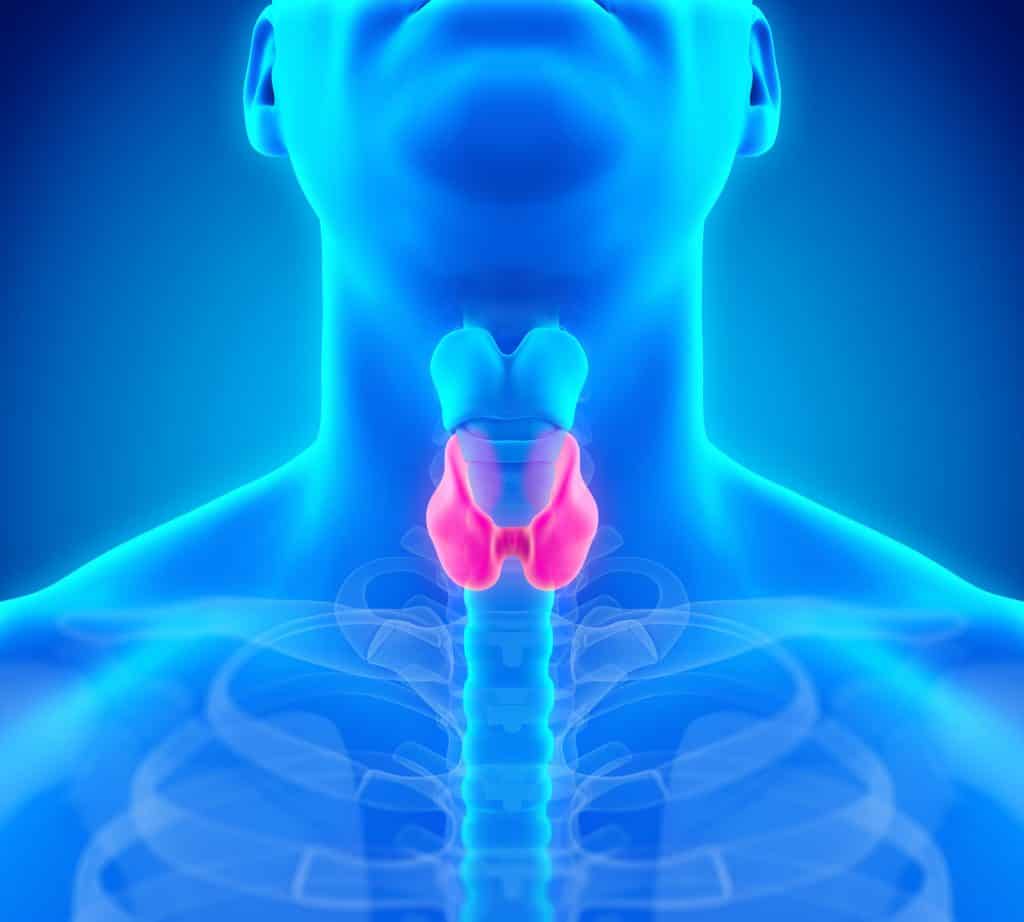 The thyroid is a gland located at the front of the neck just below the Adam’s apple. It is responsible for producing essential hormones. The thyroid has two lobes connected by narrow tissue that wraps around the windpipe.
The thyroid gland regularly secretes “thyroid hormones” that influence different aspects of the body. The “thyroid hormones” consist of triiodothyronine (T3), tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine or T4), calcitonin.
The pituitary gland is responsible for triggering a response from the thyroid. The pituitary gland tells the thyroid whether to produce more or less hormones to keep the body’s functions regulated.
The thyroid is a gland located at the front of the neck just below the Adam’s apple. It is responsible for producing essential hormones. The thyroid has two lobes connected by narrow tissue that wraps around the windpipe.
The thyroid gland regularly secretes “thyroid hormones” that influence different aspects of the body. The “thyroid hormones” consist of triiodothyronine (T3), tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine or T4), calcitonin.
The pituitary gland is responsible for triggering a response from the thyroid. The pituitary gland tells the thyroid whether to produce more or less hormones to keep the body’s functions regulated.
What is the Function of the Thyroid Gland?
As mentioned before, the function of the thyroid gland is to regulate bodily functions. These bodily functions include:- Breathing
- Heart rate
- Body weight
- Muscle strength
- Menstrual cycles
- Body temperature
- Cholesterol levels
- Metabolic rate
- Digestive function
- Bone maintenance
- Brain development
Common Problems and Conditions with the Thyroid
Many problems can arise that have to do with the thyroid gland. Problems start to occur when the thyroid begins producing too much hormone or not enough. This is known as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, respectively. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) is more common than an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). However, each can cause problems. Here are common problems with the thyroid.Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system begins attacking the thyroid, causing it to make more hormone than what the body needs. This is the most common disease associated with hyperthyroidism. Graves’ disease most commonly affects women under the age of 40, but it can affect anyone. Individuals that have Graves’ disease may experience anxiety, irritability, fatigue, and irregular heartbeat. Problems with the eyes, including bulging, inflammation, and vision changes, may also occur.Hashimoto’s Disease
Hashimoto’s disease is the most common disease associated with an underactive thyroid. This is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the thyroid, damaging it, resulting in the thyroid not making enough hormone. Hashimoto’s may result in tiredness, weight gain, constipation, depression, and other symptoms.Goiter
Goiter occurs when the thyroid gland becomes enlarged but is not cancerous. This is primarily due to a lack of iodine in a person’s diet. If goiter becomes severe, then individuals may experience tightness and swelling in the neck, difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing.Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are growths that form on or in the gland. Most of the nodules are small and benign, but in some cases, the nodules can be cancerous. Causes of thyroid nodules typically include iodine deficiency and Hashimoto’s disease. If nodules become large enough, then individuals may experience breathing or swallowing difficulties. In some cases, the nodules may cause the thyroid to produce more hormones leading to hyperthyroidism.Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can cause your metabolism to become accelerated, leading to weight loss and rapid heartbeat. Hyperthyroidism can mimic other conditions, which makes it difficult for some doctors to diagnose.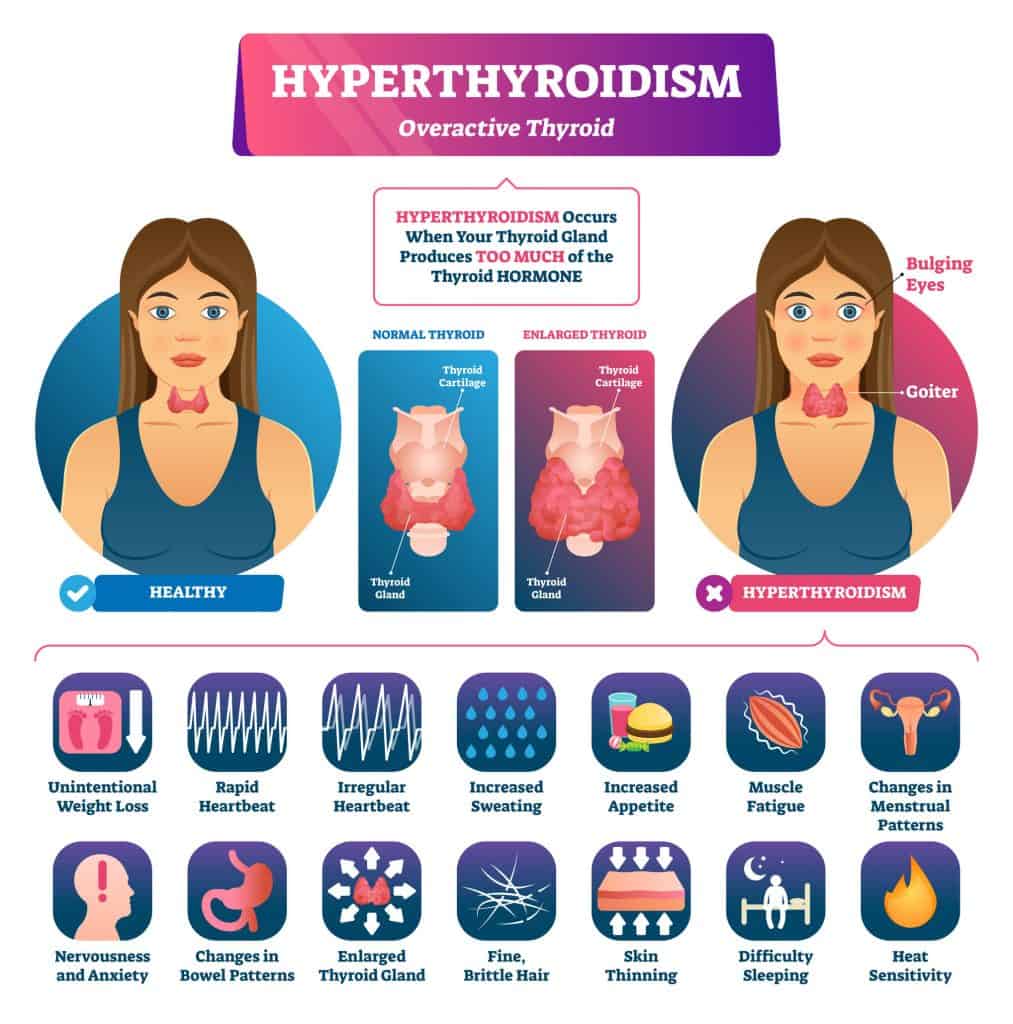 Symptoms of an overactive thyroid include:
Symptoms of an overactive thyroid include:
- Unintended weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Increased appetite
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Sweating
- Changes in menstrual cycles and patterns
- Sweaty
- Sensitivity to heat
- Fatigue
- Frequent bowel movements
- Difficulty sleeping
- Thinning of the skin
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) gradually becomes worse and worse. So, signs and symptoms may be subtle and unrecognizable until your condition becomes more severe. As your metabolism continues to slow due to the lack of thyroid hormone being produced, symptoms will become more apparent.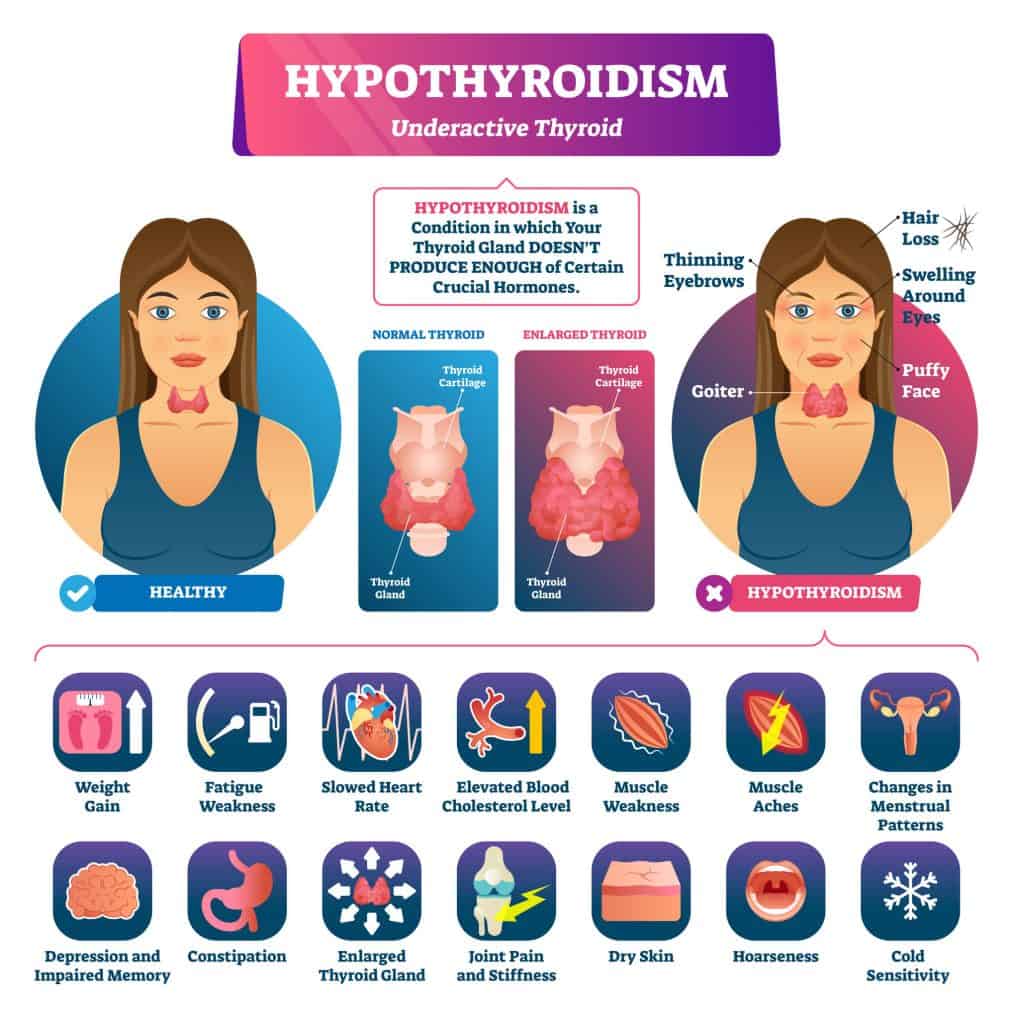 Symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- Weight gain
- Sensitivity to cold
- Dry skin
- Pain or swelling in joints
- Depression
- Slowed heart rate
- Impaired memory
- Thinning of hair
- Constipation
- Puffy face
- Irregular menstrual periods

