What is the Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
Posted by Prescription Hope - See Editorial Guidelines (Last Updated On: Fri Jul 14 2023)
 Diabetes could perhaps be one of the most misconstrued illnesses. Many people know that there are two main types, but they are unaware of the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
In order for us to really understand diabetes as a whole, we have to first breakdown the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The causes, treatments, and medications used are different for each type of diabetes.
Here’s a short answer for you before you get into the details.
What is the Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes? The main differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the causes and the treatments for the diseases. Type 1 is autoimmune and has to be treated with insulin. Type 2 is often caused by lifestyle choices and can be treated with diet and exercise or medication, depending on the severity.
Here is everything you should know about the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes could perhaps be one of the most misconstrued illnesses. Many people know that there are two main types, but they are unaware of the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
In order for us to really understand diabetes as a whole, we have to first breakdown the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The causes, treatments, and medications used are different for each type of diabetes.
Here’s a short answer for you before you get into the details.
What is the Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes? The main differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the causes and the treatments for the diseases. Type 1 is autoimmune and has to be treated with insulin. Type 2 is often caused by lifestyle choices and can be treated with diet and exercise or medication, depending on the severity.
Here is everything you should know about the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes
Before we dive into the specifics, we need to cover the basics of diabetes and why it can cause severe health problems down the road. The main organ we’re dealing with when talking about diabetes is the pancreas. The pancreas is responsible for sensing the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. When it senses a rise in glucose it will release insulin. Picture insulin as a school bus. Insulin goes out, picks up the glucose, and delivers it into the muscle and fat cells throughout the body. Once glucose is absorbed into the muscle and fat throughout the body, your body now has the energy to move or perform daily functions. With diabetes though, the pancreas either stops working altogether or cannot keep up with the amount of glucose entering the bloodstream. If you have too little glucose in the bloodstream (hypoglycemia), your body cannot produce energy, and you run the risk of passing out. If you have too much glucose in the bloodstream (hyperglycemia), you run the risk of damaging vessels that transport blood to organs. This means you are running the risk of kidney failure, heart disease, vision impairment, and so on.Symptoms of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
In general, the symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are fairly similar. The symptoms of type 1 diabetes will show up when your blood sugar level is elevated. These symptoms include:- extreme thirst
- frequent urination
- weight loss
- exhaustion
- blurry vision
- hunger
- numbness or tingling in extremities
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
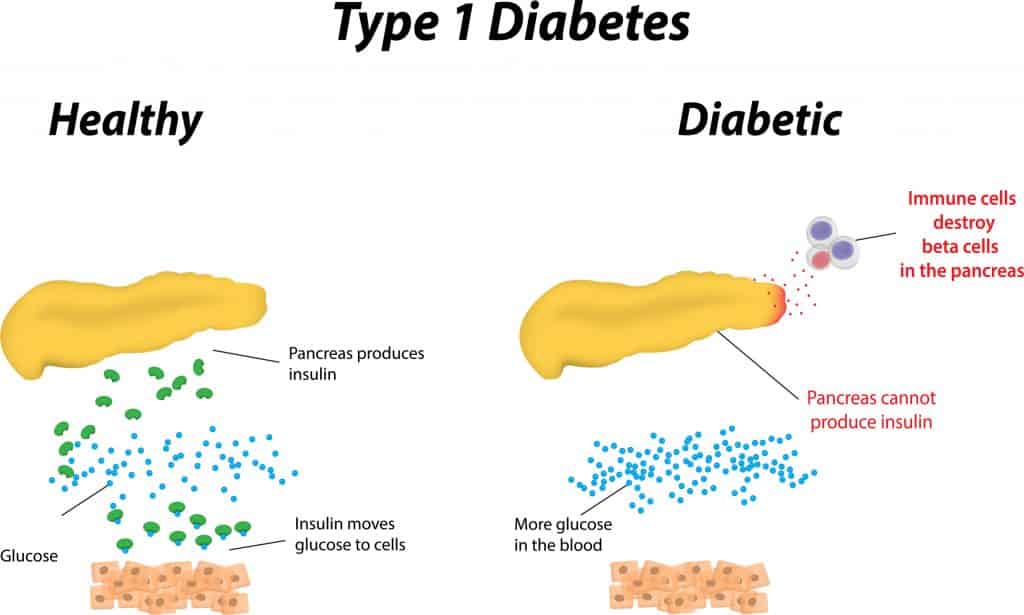 First, let’s clear up the confusion and address the fact that there is no correlation between a person’s diet and the risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not yet fully known. We do know this though, that the body essentially attacks itself. The body’s immune system, for some reason, begins attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This is what’s known as an autoimmune disease.
If someone in your family has type 1 diabetes, whether that be a grandparent, parent, or sibling you are at a higher risk of developing it also. There has also been a correlation between type 1 and certain genes.
Certain environmental factors may also play a role in someone developing type 1. Some scientists believe that when certain viruses attack the immune system, the immune system becomes confused and may begin attacking cells that are beneficial to the body.
There have been a few speculations about stress having an impact on someone’s susceptibility to type 1 diabetes, but that is difficult to accurately determine.
Again, the cause of type 1 is not fully known and research is still being done to find a root cause.
First, let’s clear up the confusion and address the fact that there is no correlation between a person’s diet and the risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not yet fully known. We do know this though, that the body essentially attacks itself. The body’s immune system, for some reason, begins attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This is what’s known as an autoimmune disease.
If someone in your family has type 1 diabetes, whether that be a grandparent, parent, or sibling you are at a higher risk of developing it also. There has also been a correlation between type 1 and certain genes.
Certain environmental factors may also play a role in someone developing type 1. Some scientists believe that when certain viruses attack the immune system, the immune system becomes confused and may begin attacking cells that are beneficial to the body.
There have been a few speculations about stress having an impact on someone’s susceptibility to type 1 diabetes, but that is difficult to accurately determine.
Again, the cause of type 1 is not fully known and research is still being done to find a root cause.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
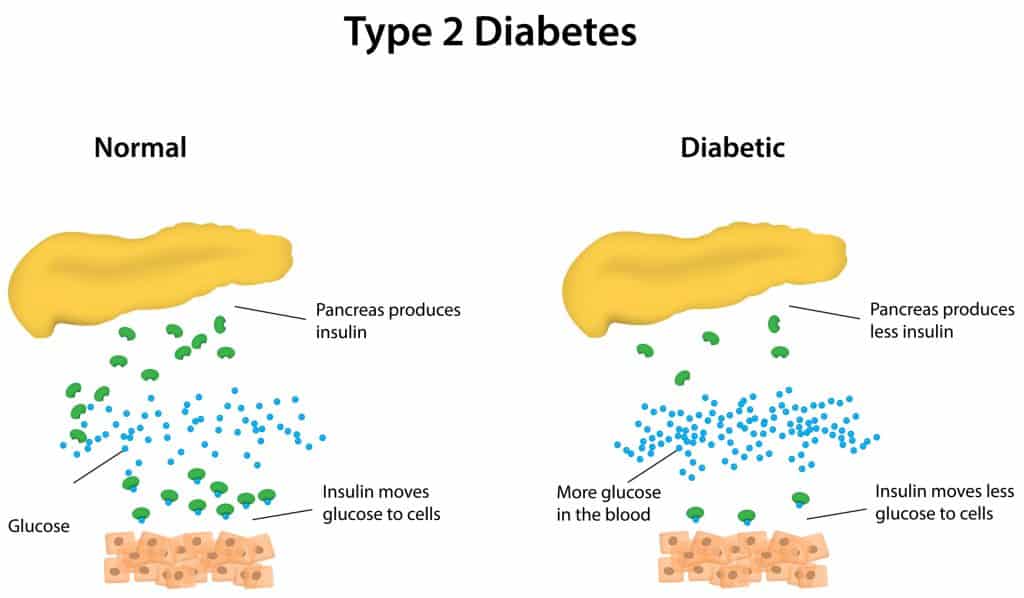 The causes of type 2 diabetes, however, are easier to determine. Family history is an important factor to consider when it comes to type 2. If someone in your family has had diabetes, you may be at a higher risk, just like with type 1.
Environmental factors are also a major cause of type 2 diabetes. There is a direct correlation to obesity and type 2. Nearly 90% of people who have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes are obese. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC), the rates of obesity have increased. Type 2 diabetes has also been on the rise, which paints the picture clearly. Carrying around excess body fat puts you at a higher risk of developing this medical condition.
In a CDC report, nearly 75% of people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes had high blood pressure. In that same report, about 50% of people diagnosed had reported that they were currently smoking or had a history of smoking cigarettes.
If you have a history of gestational diabetes (diabetes that shows up during pregnancy), then you are at a higher risk for developing type 2 down the road. Consider these factors and determine what in your lifestyle needs to change to reduce the risk of being diagnosed.
The causes of type 2 diabetes, however, are easier to determine. Family history is an important factor to consider when it comes to type 2. If someone in your family has had diabetes, you may be at a higher risk, just like with type 1.
Environmental factors are also a major cause of type 2 diabetes. There is a direct correlation to obesity and type 2. Nearly 90% of people who have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes are obese. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC), the rates of obesity have increased. Type 2 diabetes has also been on the rise, which paints the picture clearly. Carrying around excess body fat puts you at a higher risk of developing this medical condition.
In a CDC report, nearly 75% of people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes had high blood pressure. In that same report, about 50% of people diagnosed had reported that they were currently smoking or had a history of smoking cigarettes.
If you have a history of gestational diabetes (diabetes that shows up during pregnancy), then you are at a higher risk for developing type 2 down the road. Consider these factors and determine what in your lifestyle needs to change to reduce the risk of being diagnosed.
Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes
The main treatment for type 1 diabetes is insulin. Insulin can either be delivered via a syringe, insulin pens, or an insulin pump. Each person who has type 1 diabetes will have an insulin-to-carb ratio. So, they must count their carbs for every meal, snack, or drink and deliver insulin based on their ratio. For example, an individual might have a ration of 1:12. This means that for every 12 grams of carbohydrates that they consume they will give themselves one unit of insulin. The insulin pump makes life a little easier when it comes to giving these injections. It is important to note, though we will not go into detail during this post, that there are two main types of insulins. A long-acting and rapid-acting. Those that use insulin pens or syringes will more than likely use at least both of these insulins. Typically, they will give themselves one shot of the long-acting insulin each day, and a shot of rapid-acting insulin for each time they consume carbs or to correct high blood sugar. Along with injecting insulin, checking blood sugar throughout the day is also required for proper treatment. This can be done via finger sticks or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). Maintaining a healthy lifestyle will also prove to be helpful in controlling blood sugar levels. This includes a healthy diet along with regular exercise.Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes
There are a variety of ways to treat type 2 diabetes. Not all type 2 diabetics need insulin to keep their blood sugars in range. They can treat their diabetes with medications in either pill form or injections. These medications help improve the function of the pancreas, help tissues absorb glucose better, or slow down the digestion of food. These medications may include Trulicity, Jardiance, Victoza, and the list goes on. Beyond this, some type 2 diabetics have been able to control their blood sugars with a strict diet and exercise and no longer need medication. This diet would consist of foods that are low carbohydrates and high in protein and unsaturated fat. Any carbs that they do eat should have a low glycemic index. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle will also help in losing weight, which will be beneficial in controlling blood sugars, and could prevent you from developing other medical conditions down the road.Prevention
When it comes to type 1 diabetes, there is no known way to prevent it. There are trials and research taking place, but there has been limited success. The best thing to do is to be aware of your family history. Watch out for the symptoms of diabetes and try to catch it early if possible. Ask your doctor to check your blood sugar if you have recently had symptoms that you are not sure about. As far as type 2 goes though, there are ways to prevent it. In general, live a healthy lifestyle and you should avoid putting yourself at risk. Limit intake of alcohol and processed foods that contain large amounts of added sugar. Exercise on a regular basis. Work towards losing weight if you are overweight or obese. If you are smoking, then take steps to quit.Conclusion
Ultimately, type 1 and type 2 diabetes are really not all too similar. However, both can be detrimental to your health and can have serious long-term effects which can be life-threatening. If you are concerned about developing either type of diabetes or are experiencing any symptoms mentioned in this article, then talk to your doctor about running a blood test. If you are having trouble affording your insulin or any other medication, then enroll with us here and pay only $60.00 a month through Prescription Hope’s medication access service for each medication.What is type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune condition in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, leading to hyperglycemia.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the body’s cells do not respond well to insulin (insulin resistance). It is often caused by lifestyle factors.
Can you have both type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
You cannot have both type 1 and type 2 diabetes because they have different mechanisms. However, those with type 1 diabetes may become insulin resistant. Type 2 diabetes cannot turn into type 1 diabetes.

